Biomimicry is revolutionizing sustainable innovation by drawing inspiration from nature's time-tested patterns and strategies. Scientists and engineers are studying biological systems to develop breakthrough solutions for environmental challenges. These nature-inspired innovations are transforming industries from architecture to waste management.
Nature has been perfecting its designs for billions of years, evolving solutions to complex problems through countless iterations. Today, scientists, engineers, and innovators are increasingly turning to nature's wisdom to solve some of our most pressing environmental challenges. This practice, known as biomimicry, is leading to breakthrough innovations that are both sustainable and highly effective.
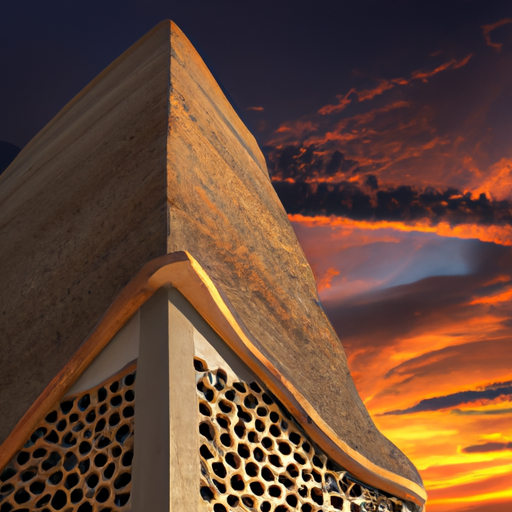
One of the most fascinating applications of biomimicry can be found in architecture and building design. The ventilation systems of termite mounds have inspired self-cooling buildings that maintain comfortable temperatures with minimal energy consumption. These structures use passive air circulation principles observed in termite colonies, reducing the need for mechanical cooling systems and significantly decreasing energy usage.
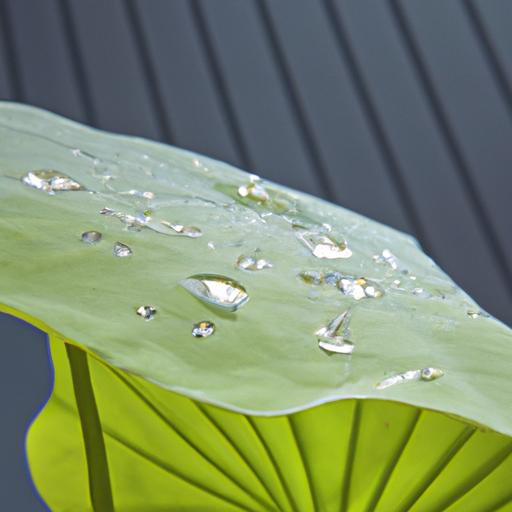
In the field of materials science, researchers are developing new sustainable materials based on natural processes and structures. Spider silk, known for its remarkable strength-to-weight ratio and flexibility, has inspired the development of bio-based fibers that could replace synthetic materials in numerous applications. Similarly, the water-repellent properties of lotus leaves have led to the creation of self-cleaning surfaces that reduce the need for chemical cleaners.
Water purification systems are being revolutionized through biomimetic approaches. The way mangrove roots filter salt from seawater has inspired more efficient desalination technologies. Meanwhile, the structure of diatoms, microscopic algae with intricate silica shells, has influenced the development of more effective water filtration systems that require less energy and fewer chemicals.
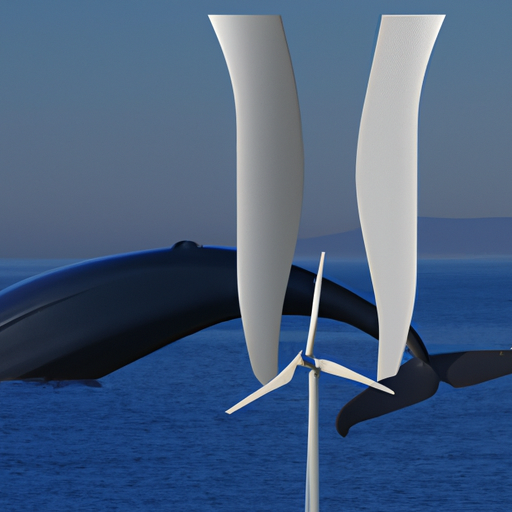
The transportation sector has also benefited from biomimicry principles. The shape of kingfisher beaks has influenced the design of high-speed trains to reduce noise and energy consumption. Marine vessels are incorporating features inspired by shark skin to reduce drag and improve fuel efficiency, while wind turbine designs are being optimized based on the structure of humpback whale flippers.
Waste management solutions are emerging from studying nature's closed-loop systems. The decomposition processes found in forest ecosystems have inspired more efficient composting technologies and biodegradation methods. These innovations are helping to address the growing challenge of waste disposal while creating valuable resources from what was once considered garbage.
Energy generation and storage systems are being transformed through biomimetic innovation. The process of photosynthesis has inspired more efficient solar cells, while the structure of plant leaves has led to improvements in solar panel design. Natural energy storage systems, such as those found in certain bacteria, are providing insights for developing better batteries and energy storage solutions.
In the realm of agriculture, biomimicry is leading to more sustainable farming practices. The complex relationships between plants and soil microorganisms have inspired new approaches to crop nutrition and pest management. These nature-inspired farming methods reduce the need for chemical inputs while improving soil health and crop resilience.
The field of robotics is increasingly incorporating biomimetic principles to create more efficient and adaptable machines. Robots inspired by insects, birds, and other animals are being developed for environmental monitoring, pollution cleanup, and ecosystem restoration. These bio-inspired machines can operate in challenging environments while minimizing their environmental impact.
The application of biomimicry extends to urban planning and infrastructure design. Cities are being reimagined as living ecosystems, with green corridors and wildlife passages integrated into urban landscapes. These design approaches help maintain biodiversity while creating more resilient and sustainable urban environments.
Perhaps most importantly, biomimicry is changing how we think about innovation and problem-solving. By studying nature's strategies for resilience, efficiency, and adaptation, we are learning to develop solutions that work in harmony with natural systems rather than against them. This shift in perspective is crucial for creating truly sustainable technologies and practices.
As we face increasingly complex environmental challenges, the role of biomimicry in sustainable innovation continues to grow. Research institutions and companies worldwide are investing in biomimetic research and development, recognizing its potential to revolutionize how we approach sustainability. The future of environmental innovation may well depend on our ability to learn from and emulate nature's time-tested solutions.



